
Mechanical sparks and friction are one of the most common causes of ignition of flammable gases and dust clouds. Accident statistics in Germany indicate that mechanical sparks and friction as an ignition source occurred in 32.7% of incidents.
Incorrectly selected, or fans deemed unsuitable for hazardous areas, can produce an effective ignition source caused by various incidents; hot surfaces, by mechanically generated sparks because of friction, impact, or abrasion processes (because of contact between the rotor – the rotating part, and fixed components) or by the electric discharge of static electricity when using non-conductive materials.
In the normal operation, or in the event of malfunctions (whether standard or rare), possible friction caused by areas meeting one another can occur. As stated in the ATEX directive and adopted into UK legislation, potential areas of contact between the rotating elements and fixed components of equipment for use in potentially explosive environments, should be manufactured from materials in which the risk of ignition caused by friction and friction impact sparks, hot spots or hot surfaces is minimised. This applies specifically to the construction and manufacture of explosion proof industrial fans. Ignition risks cannot be completely eliminated but can be significantly reduced by taking suitable constructive measures for avoiding ignition sources.
European and UK Directives are clear on the permissible material pairings that are suitable to reduce the ignition source caused by friction of rotating and fixed component parts. Material pairings are considered carefully by fan manufacturers and authorised bodies. They use their theoretical and practical knowledge, coupled with the known application conditions for the environment in question, the safest material pairing and other compulsory technical specifications to determine how a product is chosen for an explosive environment.
Material pairings are devised and communicated in legislationdocumentation to minimise the risk of an explosion. Industrial fans in systems or machinery, are generally not supervised continuously and contact between rotating and stationary orfixed components, may occur in a particular area for an unknown amount of time, potentially in long intervals.
Metal to Metal Ignition
Metal to metal ignition is caused either by rubbing friction, as mentioned earlier, such as between a rotating impeller and a stationary piece of metal, or by impact of two metal objects. Research has shown that in metal-to-metal contact, the properties of the more readily oxidised metal, normally determine the degree of ignition hazard. The hardness, melting point, ignition temperature, specific heat conductivity and brittleness of the metals all play a role, in that they determine the size, duration, temperature and heat capacity of the incendive sparks.
An important precondition for all the protection principles is that parts which are in unhindered contact with the explosive atmosphere must not be able to reach non-permitted high temperatures with respect to the ignition temperature of substances present in the site of installation. This means that the ignition temperature is relevant for all protection principles. We cover temperature classes and surface temperature on our website.
The standard EN14986 dictates minimum design rules that industrial fans for hazardous areas should comply with. In relation to the material pairings that we introduced earlier, the below briefly seeks to improve your knowledge of the parts of ATEX fans that indicate the rotating and stationary parts that must be manufactured from these permissible materials to reduce the risk of sparks and hot spots due to frictional rubbing in the event of movement between the two parts. For more information on a wide range of ATEX topics please visit our website.
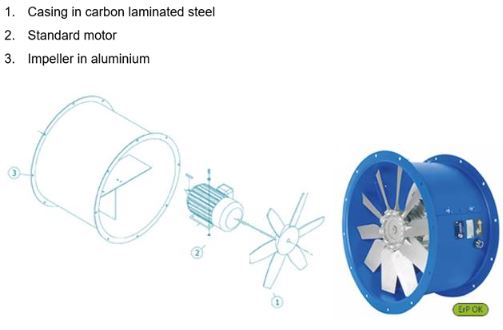
ATEX Axial Fans
In axial fans the two parts are:
Rotating: Impeller, tip of the blades.
Stationary: The fan casing & ring
This article can also be found in the Jan/Feb isuse.

